Tutorial Electrostatic Discharge
Sometimes harmful voltage surges come from electrostatic discharge (ESD). This is a single, fast, high current transfer of electrostatic charge resulting from one of two conditions. These conditions are:
-
Direct contact transfer between two objects at different potentials (sometimes called contact discharge)
- A high electrostatic field between two objects when they are in close proximity (sometimes called air discharge)
The prime sources of static electricity are mostly insulators and are typically synthetic materials, e.g., vinyl or plastic work surfaces, insulated shoes, finished wood chairs, Scotch tape, bubble pack, etc. Voltage levels generated by these sources can be extremely high since their charge is not readily distributed over their surfaces or conducted to other objects. The generation of static electricity caused by rubbing two substances together is called the triboelectric effect. Some common examples of ordinary acts producing significant ESD voltages are:
Walking Across a Carpeted Floor 1,000 V –1,500 V
Walking Across a Vinyl Floor 150 V –250 V
Note: Above data assumes 60% relative humidity (RH). For 30% or lower RH, voltages can be greater than ten times those listed here.
BIOPAC MP Series data acquisition platforms are designed and tested to adhere to IEC 61000-4-2. Generally considered, equipment adherence to this standard establishes a robust platform for ESD protection.
IEC 61000-4-2: ESD Standard for System Level Testing
The IEC standard is a system level test that replicates a charged person discharging to a system in a system end user environment. The purpose of the system level test is to ensure that finished products can survive normal operation and it is generally assumed that the user of the product will not take any ESD precautions to lower ESD stress to the product.
The IEC 61000-4-2 standard defines four standard levels of ESD protection, using two different testing methodologies. Contact discharge involves discharging an ESD pulse directly from the ESD test gun that is touching the device under test. This is the preferred method of testing. However, the standard provides for an alternate test methodology known as air discharge for cases where contact discharge testing is not possible. In the air discharge test, the ESD test gun is brought close to the device under test until a discharge occurs. The standards are defined so that each level is considered equivalent – a Level 4 contact discharge of 8 kV is considered equivalent to a 15 kV air discharge.
The following table indicates test levels.
IEC 61000-4-2 Test Levels
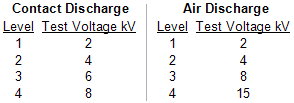
Stay Connected