How can I move QRS peak event marks from the bottom of S waves to the top of R waves?
Sometimes algorithms designed to locate ECG complex boundaries place QRS peak event marks at the wrong locations, such as:
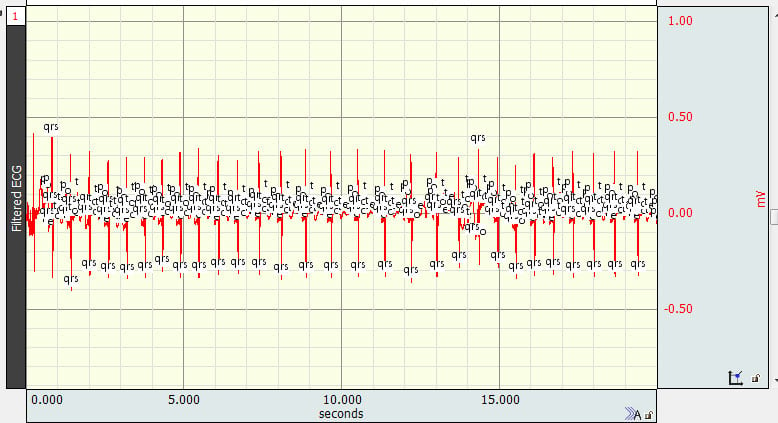
While it is not possible to wholesale move event marks when this occurs, there is a much more efficient and effective way to achieve the same outcome than to move the event marks one at a time.
A. Using Find Cycle, a new set of event marks may be placed using the originals as starting points, and
B. Using the Event Palette, the old ones may be removed.
Use Find Cycle to create a new set of event marks at the peaks closest to the original event marks.
- Type Ctrl+f (Windows) or Command+f (Mac) to launch the Cycle Detector.
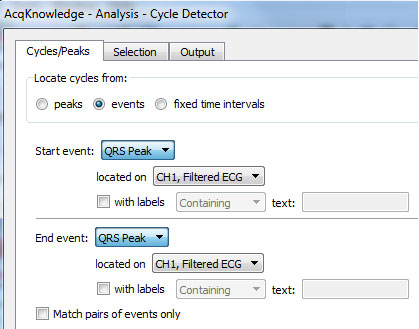
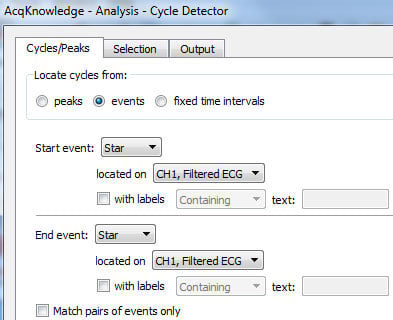
- Under the “Cycles/Peaks” tab, specify that the software should find QRS peak event marks on the appropriate channel and to find them one at a time (i.e., UNcheck the “Match pairs of events only” box):
- Under the “Selection” tab, specify that the cycle detector should look in a small window around each event mark (here the selection includes one tenth of a second both before and after each event):
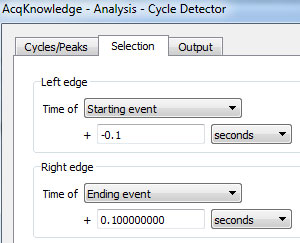
- Click the “Move Cursor to Origin” button while on this tab in order to ensure that all event marks will be found.
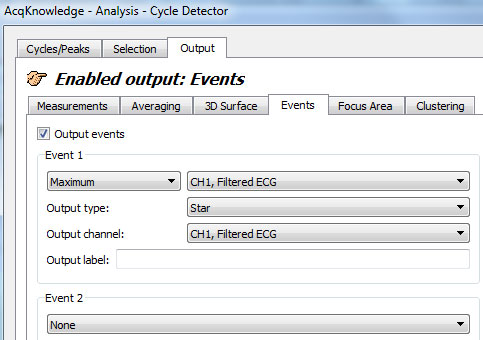
- Under the “Output” tab, specify that the software should place an event mark at the maximum within this window. The type of event mark is arbitrary except that it should be of a type that has NOT been used before on the channel in question. Here, stars are placed:
- Click “Find All Cycles”:
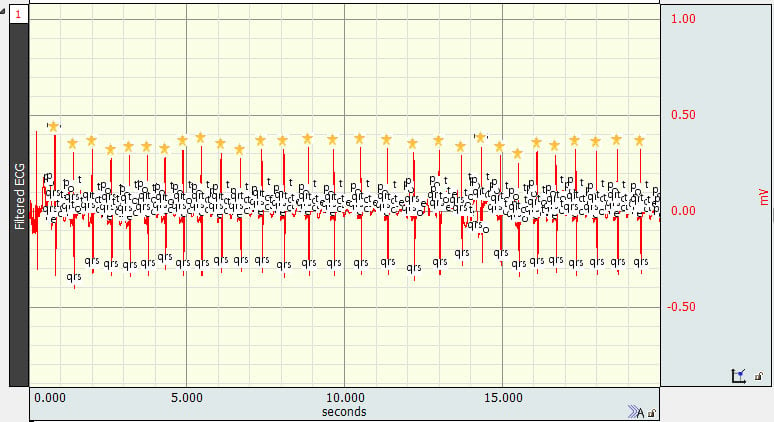
If it is necessary or useful that the event marks for subsequent analyses actually be QRS peak event marks, then the original incorrectly placed marks should be removed.
- Open the Event Palette
via the toolbar display shortcut button:
or via the event bar: or via the menu: Display > Show > Event Palette.”
or via the menu: Display > Show > Event Palette.” - Under the “Actions” menu, click the “Clear…” button:
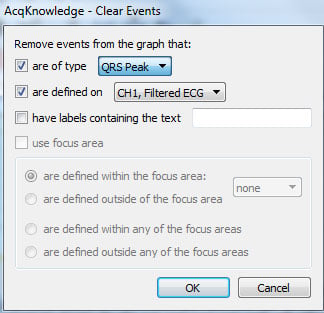
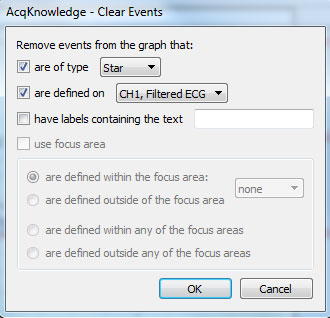
- Specify that QRS Peak events should be removed on the appropriate channel and then click “OK.”
- Accept the requested modification by clicking “Yes.”
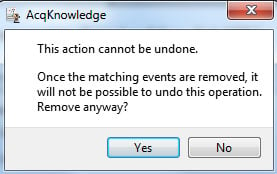
- Launch the Cycle Detector again (Ctrl+f or Command+f, as appropriate), and search for the event marks placed per above:
- On this pass, select ONLY the location of each event mark, not any surrounding area:
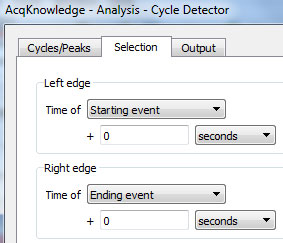
- Click the “Move Cursor to Origin” button.
- Under the “Output” tab, place event marks at the location (“Interval start” and “At location” are specified as “Left edge” and “At edge” in older software):
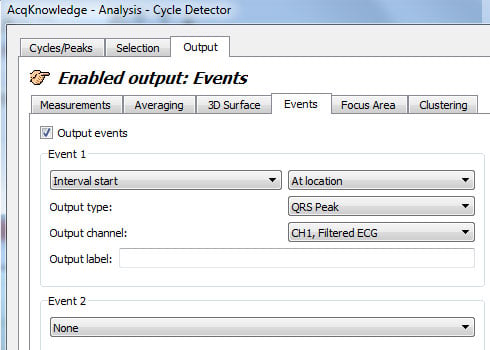
- Click “Find All Cycles.”
- Remove the first set of event marks placed by opening the Event Palette again and using the “Clear” button:
WHAT'S NEW
Speech and communication are integral parts of human relationships and development As such,...
Stay Connected