
The BSL System offers over 60 industry-standard transducers. Further, the BSL System interfaces with other major amplifier and transducer manufacturers encompassing the most commonly used biomedical engineering instruments by using a wide variety of interface connectors and cables. Choose from 18 ready-made interface connectors, or build your own with the custom interface kit.

The BSL System offers over 60 industry-standard transducers. Further, the system easily interfaces with other major amplifier and transducer manufacturers encompassing the most commonly used exercise physiology lab products such as force plates, ergometers, motion analysis systems, and metabolic carts. The BSL System can trigger or receive trigger information from other equipment. For interfacing, choose […]

Use the Current/Voltage Drive & Monitor Cable to perform ion transport studies. The cable uses the output from the BSL hardware to drive a set of stimulation electrodes and also monitors stimulation current. Use the new High Impedance Cable to record from the cockroach ventral nerve and for a variety of intracellular and extracellular recordings.
Biopac Science Lab comes with two lessons focused on muscle activity: Lesson 1 — EMG I Electromyography: Motor Unit Recruitment Lesson 1 investigates the properties of skeletal muscle. Students record the EMG data associated with the maximum clench strength for their dominant hand and non-dominant hand. The system records and displays both the raw and […]
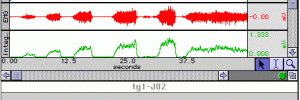
Record EMG to investigate the properties of skeletal muscle. Record and display raw and integrated EMG signals; overlap the signals for better correlation of the data. Measure strength and repeat trials for motor unit recruitment /summation and fatigue. Demonstrate the treppe (staircase) phenomenon. Study the contractility of skeletal muscle with the force transducer and stimulator. […]
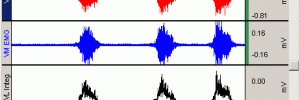
Students can measure EMG and Integrated EMG, including force and angle of limb movement. Students can listen to the sound of the electrical activity coming from muscle as they squeeze a hand dynamometer and equate changes in sound with changes in force. Add the BSL stimulator and human-safe stimulation electrode for a variety of muscle […]
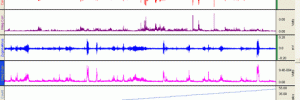
Record surface EMG data to investigate the properties of skeletal muscle. Record and display raw and integrated EMG signals; overlap the signals for better correlation of the data. Measure strength and repeat trials for motor unit recruitment, summation and fatigue. Use the reflex hammer transducer to study reflex response (neural control), or add the dynamometer […]
Students can measure EMG and Integrated EMG, including force and angle of limb movement. They can listen to the sound of the electrical activity coming from the muscle as they squeeze a hand dynamometer and equate changes in sound form and intensity with changes in force. Add the BSL stimulator and human-safe stimulation electrode for […]

Combine the human-safe stimulating electrode with the stimulator to record nerve conduction experiments. Stimulate the ulnar nerve and record nerve conduction time (see Lesson H03). This allows students to stimulate a subject at three different points along the ulnar nerve. The distance between the stimulation and recording points are measured and the velocity of signal […]

Combine the human-safe stimulating electrode with the stimulator to record nerve conduction experiments. Stimulate the ulnar nerve at three different points and record nerve conduction time. Measure the distance between the stimulation and recording points and then calculate velocity.








Stay Connected